When to use LeNet ?
LeNet, also known as LeNet-5, is a convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture that was developed by Yann LeCun et al. in 1998 for the recognition of handwritten digits. It consists of several layers of convolution, pooling, and fully connected layers. LeNet has since become a popular model for image classification tasks, and its architecture has been adapted and improved upon in many subsequent models.
LeNet is particularly useful for tasks that involve image recognition, such as object detection or character recognition. It is a good choice for such tasks because it is designed to work with 2D images and is able to effectively capture the spatial relationships between pixels.
One example of a task that could benefit from the use of LeNet is handwritten character recognition. In this task, the goal is to correctly identify handwritten characters, such as letters or digits. LeNet can be used to train a model on a dataset of handwritten characters and then use that model to predict the correct character for a given input image.
Here’s how it works:
The input image is first passed through a convolutional layer, which applies a set of filters to the image and produces a set of feature maps. This is followed by a pooling layer, which reduces the dimensionality of the feature maps by applying a pooling function (such as max pooling) to each one. This process of convolution and pooling is repeated several times to extract more and more complex features from the input image.
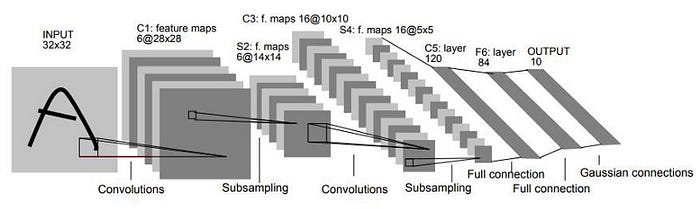
The resulting feature maps are then passed through a series of fully connected layers, which perform the final classification of the image. The output of the last fully connected layer is a set of probabilities, indicating the likelihood that the input image belongs to each of the possible classes (in the case of handwritten character recognition, the classes would be the digits 0–9).
Explanations LeNet functionality -

Description-
In this architecture, the input is a 32x32 grayscale image, and the output is a probability distribution over 10 possible classes. The Conv1 layer applies 6 filters of size 5x5 to the input image, producing 6 output feature maps of size 28x28. The Pool1 layer then performs 2x2 max pooling with a stride of 2, reducing the size of the feature maps to 14x14.
The Conv2 layer applies 16 filters of size 5x5 to the output of Pool1, producing 16 output feature maps of size 10x10. The Pool2 layer then performs 2x2 max pooling with a stride of 2, reducing the size of the feature maps to 5x5.
The output of Pool2 is then flattened and passed through two fully connected layers (FC1 and FC2), each with a Tanh activation function. Finally, the output of FC2 is passed through a Softmax activation function to produce the final probability distribution over the 10 possible classes.
Overall, the LeNet-5 architecture is a relatively simple but effective convolutional neural network for image classification tasks, and has served as a basis for many subsequent CNN models.
In summary, LeNet is a powerful architecture for image classification tasks, particularly those involving spatial relationships between pixels. It has been successfully used for tasks such as character recognition and object detection, and its architecture has served as a basis for many subsequent CNN models.

Comments
Post a Comment